
Alignment Adjustment
1, Flexible couplings transmit torque and rotational angle while absorbing misalignment. When the misalignment exceeds allowable values, vibration may result or the life of the coupling may become shortened, Make sure to adjust the alignment accordingly.
2,There are three types of shaft misalignment, namely in terms of parallel misalignment, angular misalignment and shaft end-play . Adjust the alignment to be below allowable values listed in the specification table of each product provided in this catalog.
3, The maximum misalignment listed in this catalog is the allowable value when only one of the misalignments exists. ln case two or more misalignments exist at the same time, the allowable values will be less than 1/2 of the maximum misalignment listed in the specification tables.
4, Misalignments are sometimes caused not only by equipment assembly, but also by vibration, heat expansion, wear of bearings, etc. during operation. Therefore, it is recommended to adjust the shaft misalignment to be below1/3 of maximum values.
Explanation of deviations occurring during the shaft-to-shaft connection process
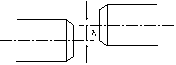
1.Parallel offset Misalignment
During installation, parallel shafts with offset centerlines cause radial misalignment, as illustrated.
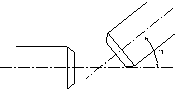
2.Symmetrical Angular Misalignment
During installation, shafts intersecting at an angle produce angular misalignment, as illustrated.
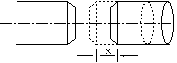
3.End-play
Axial misalignment refers to deviations caused by mechanical reciprocating motion between shafts,as illustrated.
4.Combined Misalignment
Combined misalignment results from deviations combining the three aforementioned factors, as illustrated.
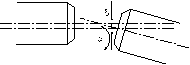

<li id="cucog"></li>